What is Kombucha?
Kombucha is a fermented tea drink that has gained popularity for its potential health benefits and unique taste. Originating in China over 2,000 years ago, it has since spread worldwide, becoming a staple in health-conscious communities. The fermentation process involves adding a SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) to tea, sugar, and water, creating a tangy, effervescent drink that is often flavored with fruits, herbs, or spices.

The fermentation process is key to kombucha’s characteristics. As the SCOBY ferments the tea, it consumes the sugar, releasing probiotics, enzymes, and acids that give kombucha its signature sour taste and potential health benefits. It’s typically brewed with green or black tea but can also be made with other types, depending on preference.
Is Kombucha Good for You?
potential health benefits of kombucha stem from its rich probiotic content. Since it’s a fermented beverage, kombucha is teeming with beneficial bacteria and yeasts, which may help support gut health. However, scientific research on kombucha’s specific benefits is still ongoing. Here’s a breakdown of potential benefits:
- Probiotics: The good bacteria in kombucha may promote a healthy gut microbiome, aiding digestion and boosting immunity.
- Antioxidants: Kombucha made with green or black tea retains the antioxidants present in tea, which help fight oxidative stress in the body.
- Detoxification: Kombucha contains acids that may help detoxify the liver and eliminate harmful substances from the body.
- Potential Immune Support: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants and probiotics in kombucha may support a stronger immune system.
- Weight Management: The fermentation process reduces sugar levels, and kombucha is generally low-calorie, making it a healthier alternative to sugary drinks.
It’s important to note that kombucha may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with compromised immune systems or certain digestive disorders. Moderation is key, and it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before adding kombucha to your diet regularly.

Does Kombucha Have Caffeine?
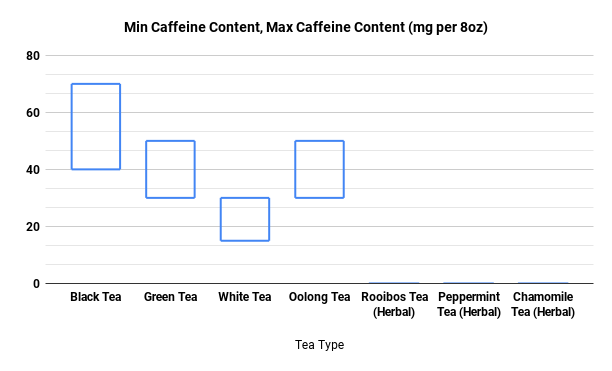
Yes, kombucha typically contains caffeine, but the amount varies depending on the tea used. Since kombucha is traditionally made with green or black tea, which naturally contain caffeine, the finished drink will also have some level of caffeine. However, the fermentation process reduces the caffeine content slightly.
On average, kombucha contains about 10-15 milligrams of caffeine per 8-ounce serving, which is significantly less than a cup of coffee (which can have 95 milligrams or more). For those who are sensitive to caffeine, this makes kombucha a more suitable alternative to highly caffeinated beverages.
If you prefer a caffeine-free version, kombucha can be brewed with herbal teas, such as rooibos, which naturally lack caffeine. Keep in mind that switching to a non-caffeinated tea may alter the fermentation process and the flavor of the final product.
How to Make Kombucha at Home
Making kombucha at home is a simple yet rewarding process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Ingredients:
- 1 SCOBY (available online or from a kombucha-making friend)
- 8 cups of water
- 1 cup of sugar (preferably organic cane sugar)
- 4 tea bags (black, green, or a combination)
- 1 cup of starter kombucha (plain, unflavored)
Instructions:
- Boil the Water: Bring 8 cups of water to a boil and dissolve the sugar.
- Add the Tea: Steep the tea bags in the hot water for 5-10 minutes, depending on how strong you want the flavor.
- Cool the Tea: Let the tea cool down completely. It’s essential to avoid adding the SCOBY to hot tea, as heat can kill the culture.
- Add the SCOBY and Starter Kombucha: Pour the cooled tea into a large glass jar and add the starter kombucha and SCOBY. Cover the jar with a cloth and secure it with a rubber band to allow air to flow while keeping out debris and pests.
- Fermentation Time: Place the jar in a warm, dark spot and let it ferment for 7-10 days. The longer you let it ferment, the more acidic and less sweet it will taste.
- Taste Test: After a week, taste the kombucha using a straw. If it’s to your liking, it’s ready! If you prefer it more sour, let it ferment for a few more days.
- Bottling: Pour the kombucha into bottles, leaving the SCOBY and a bit of liquid behind for your next batch. You can add fruit, herbs, or spices at this stage for flavoring.
- Second Fermentation (Optional): For a fizzier kombucha, seal the bottles tightly and let them sit at room temperature for another 2-3 days to carbonate. Be cautious of pressure build-up!
Does Kombucha Have Alcohol?

Yes, kombucha contains a small amount of alcohol as a natural byproduct of fermentation. During the fermentation process, the yeast in the SCOBY consumes sugar and produces alcohol, which is then metabolized by the bacteria into acids. Typically, store-bought kombucha contains less than 0.5% alcohol, classifying it as a non-alcoholic beverage.
However, homemade kombucha can sometimes contain higher levels of alcohol if fermented for longer or under certain conditions. This is because prolonged fermentation can lead to an increased alcohol content. While the alcohol in kombucha is generally too low to have an intoxicating effect, it’s important to be mindful if you’re sensitive to alcohol or avoiding it for other reasons.
If you’re concerned about the alcohol content, there are brands that produce “hard kombucha,” which is brewed to have a higher alcohol content (similar to light beer or cider).
Health Benefits of Kombucha
Kombucha enthusiasts often claim a wide range of health benefits associated with the drink. While some benefits are well-documented due to the fermentation process and the presence of probiotics, others require more scientific evidence. Let’s explore the health benefits associated with kombucha:
1. Improved Gut Health
Kombucha’s probiotics help replenish the good bacteria in your gut, promoting a healthy digestive system. A well-balanced gut microbiome is crucial for nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall health.
2. Antioxidants
When kombucha is made from green or black tea, it inherits the antioxidant properties of these teas. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, which can lead to cellular damage and chronic diseases.
3. Detoxification
Kombucha contains glucuronic acid, which is thought to aid the liver in detoxifying the body by binding to toxins and flushing them out.
4. Joint Health
Kombucha may promote joint health due to its content of glucosamine, a compound that helps support healthy cartilage. Some claim that regular kombucha consumption may help reduce joint pain associated with conditions like arthritis.
5. Boosting Immune System
The probiotics and antioxidants in kombucha may help strengthen the immune system by supporting the gut’s health and reducing oxidative stress.
6. Mental Health and Mood Support
Some believe kombucha’s B-vitamins, especially B12, could help boost energy levels and improve mental clarity. Additionally, kombucha’s gut-health benefits could also contribute to improved mental health, as research shows a strong link between gut health and mood regulation.


Conclusion
Kombucha is a fermented tea with potential health benefits, ranging from improved gut health to enhanced detoxification processes. With its probiotic content, antioxidants, and low-calorie nature, kombucha makes for a refreshing alternative to sugary drinks. However, the drink does contain small amounts of caffeine and alcohol, and it may not be suitable for everyone, so it’s essential to consume it mindfully. Whether you’re brewing at home or buying it ready-made, kombucha’s unique flavor and benefits make it a fascinating addition to a healthy lifestyle.





